The Role of Prototyping in Design: From Concept to Creation
Prototyping is a fundamental process in the field of UX/UI design, serving as a pivotal bridge between conceptualization and final product creation. By creating tangible representations of design concepts, prototypes enable designers to test, iterate, and refine ideas before implementation, ultimately enhancing the usability, functionality, and overall user experience of digital products. This comprehensive guide explores the significance of prototyping in design, its various types, best practices, and its transformative impact on the design process.
Understanding Prototyping in Design
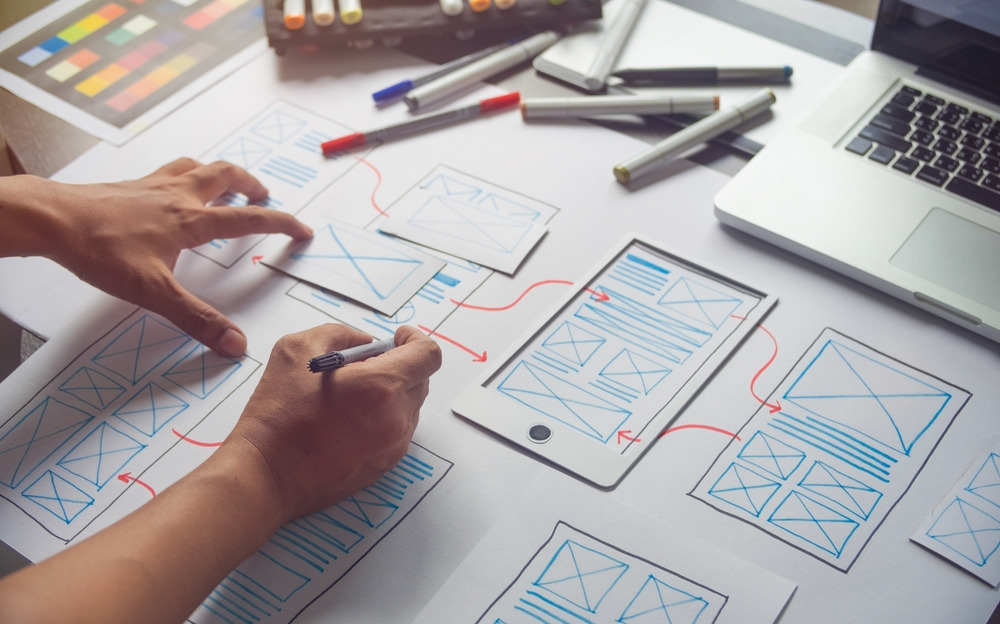
Prototyping involves creating scaled-down versions of a product or interface to simulate its behavior, functionality, and user interaction. Unlike final products, prototypes are iterative and serve as experimental models that allow designers to explore design ideas, gather feedback, and validate assumptions early in the development process. Prototyping plays a crucial role in mitigating risks, reducing costs, and ensuring that the final product meets user expectations effectively.
Key Types of Prototypes
- Low-Fidelity Prototypes:
- Sketches and Wireframes: Simple, static representations of design concepts that focus on layout, content structure, and navigation without detailed visual elements.
- Paper Prototypes: Hand-drawn sketches on paper that simulate user interactions and workflows through manually operated elements.
- Medium-Fidelity Prototypes:
- Clickable Wireframes: Interactive prototypes that simulate user interactions and navigation flows, often created using prototyping tools like Sketch, Adobe XD, or Figma.
- Digital Prototypes: More refined digital representations with basic visual elements and interactive components to test usability and functionality.
- High-Fidelity Prototypes:
- Pixel-Perfect Designs: Prototypes that closely resemble the final product in terms of visual design, layout, and interactive elements.
- Interactive Prototypes: Fully functional prototypes with advanced interactions and animations, offering a realistic user experience similar to the final product.
Benefits of Prototyping
- User Feedback and Validation: Enables designers to gather early feedback from stakeholders and users, validating design assumptions and identifying usability issues before development.
- Iterative Design Process: Facilitates iterative refinement and optimization of design concepts based on feedback and usability testing results.
- Risk Mitigation: Reduces the risk of costly design flaws and usability issues by identifying and addressing potential issues early in the design process.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Improves communication and collaboration between designers, developers, and stakeholders by providing a tangible reference for discussing design decisions and requirements.
Best Practices for Prototyping
- Set Clear Objectives: Define the goals and objectives of prototyping to guide the design process and focus efforts on key areas of improvement.
- Start with Low-Fidelity Prototypes: Begin prototyping with low-fidelity versions to quickly explore ideas and concepts without investing significant time and resources.
- Test Early and Often: Conduct frequent usability tests with prototypes to gather actionable feedback and validate design decisions throughout the design lifecycle.
- Involve Stakeholders: Engage stakeholders, including clients, product managers, and end-users, in the prototyping process to ensure alignment with project goals and user needs.
- Document and Iterate: Document feedback and insights obtained from usability testing sessions and use them to iteratively refine and improve prototypes.
The Prototyping Process: Steps and Considerations
- Define Requirements: Gather requirements and user insights through research and analysis to inform the prototyping process.
- Design and Develop: Create prototypes based on defined requirements, utilizing appropriate prototyping tools and techniques.
- Test and Evaluate: Conduct usability tests with prototypes to identify usability issues, gather feedback, and validate design decisions.
- Iterate and Refine: Incorporate feedback and insights into iterative refinements of prototypes, making necessary adjustments to improve usability and functionality.
- Finalize and Handoff: Finalize high-fidelity prototypes for development handoff, ensuring that design specifications and interactions are clearly documented for implementation.
Case Studies and Examples
Illustrate the effectiveness of prototyping with real-world case studies that demonstrate how prototypes have been used to improve user experiences, streamline development processes, and achieve business objectives. Highlight successful outcomes and lessons learned from implementing prototyping strategies in various design projects.
Prototyping is a critical component of the design process that empowers UX/UI designers to create innovative and user-centered digital experiences. By leveraging prototypes to explore ideas, validate assumptions, and iterate designs based on user feedback, designers can mitigate risks, optimize usability, and deliver products that resonate with users. As technology evolves and user expectations continue to evolve, integrating prototyping into the design workflow remains essential for achieving design excellence, fostering collaboration, and driving innovation in the competitive landscape of digital design. Embrace prototyping as a strategic tool to bridge the gap between concept and creation, ultimately creating impactful and successful digital products that meet the needs and exceed the expectations of users.